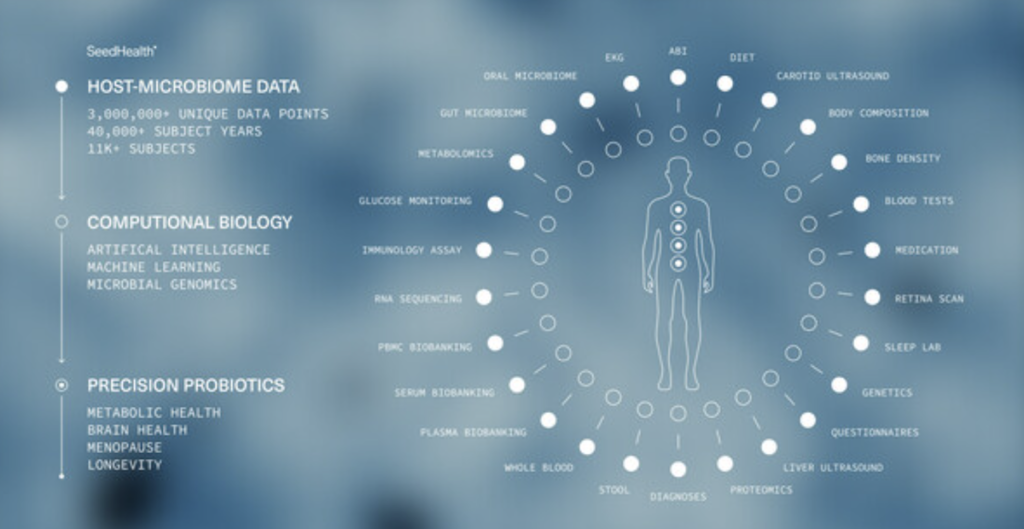
Seed Health has launched CODA, a computational biology platform aimed at discovering and developing precision probiotics and microbiome-directed interventions. Powered by the Human Phenotype Project, the world’s most extensive multi-omics dataset, CODA focuses on advancing research in metabolic health, brain health, menopause, and longevity.
CODA integrates over three million phenotypic data points from more than 13,000 individuals across 40,000 cumulative subject years. This dataset combines microbiome analysis with genetic, immune, metabolomic, and proteomic data to explore the microbiome’s role in various health factors. Raja Dhir, Co-Founder of Seed Health, stated, “Our CODA platform provides a comprehensive, multi-omics perspective, uncovering critical connections between the microbiome and health.”
The collaboration between Seed Health and the Weizmann Institute of Science leverages advanced AI and ML algorithms to process immense amounts of data, including 200TB of human data from The Human Phenotype Project. Prof. Eran Segal, Ph.D., emphasized the platform’s ability to develop organ-specific clocks, revealing the microbiome’s impact on aging rates and health outcomes across different organ systems.
The menopause program within CODA aims to mitigate menopause-induced symptoms and age acceleration. Initial findings have identified a significant acceleration in Biological Age (BA) during menopause, signaling the need for targeted interventions. Dirk Gevers, Ph.D., Chief Scientific Officer of Seed Health, highlighted CODA’s comprehensive approach, stating, “CODA empowers us to unravel the complex interactions between diet, supplementation, the microbiome, and multi-system human health more effectively than before.”
Ara Katz, Co-CEO and Co-Founder of Seed Health, emphasized the platform’s potential to translate research findings into interventions with a meaningful impact on human health globally. With its focus on menopause, Seed Health aims to address the specific needs of women during this critical life stage.



